What Is GPU Hotspot? – Complete Guidelines 2025!
In graphics processing units (GPUs), the term GPU hotspot refers to the hottest point detected on a GPU die. Modern GPUs, with their complex architecture, can develop localized regions where temperatures are significantly higher than the average core temperature.
Monitoring this hotspot is essential for optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity of hardware.
A GPU hotspot is the highest temperature recorded at a specific point on the GPU die, detected by internal sensors. It represents the hottest area of the GPU and is usually higher than the average core temperature.
To learn more about GPUs, start exploring with TechStarGT.
What Causes a GPU Hotspot?
The formation of a GPU hotspot is primarily driven by uneven heat distribution across the GPU die. Several factors contribute to this phenomenon:
- Manufacturing Variations: Even tiny imperfections during production can cause certain parts of the GPU to generate more heat.
- Thermal Paste Degradation: Over time, the thermal paste between the GPU die and the cooler may dry out, leading to poor heat transfer.
- Cooler Design: Inadequate or poorly distributed cooling solutions can create areas of higher thermal stress.
- Overclocking: Pushing the GPU beyond its factory settings increases the power draw and generates additional heat, often causing hotspots.
Understanding these causes is crucial in diagnosing temperature anomalies and implementing effective cooling solutions.
How Is GPU Hotspot Temperature Measured?
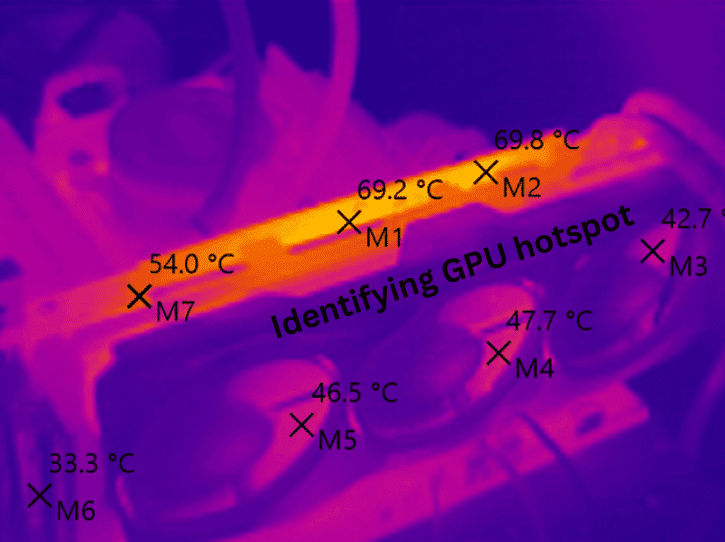
Modern GPUs are equipped with multiple thermal sensors strategically placed across the silicon.
Unlike older GPUs that reported a single average temperature, newer models such as NVIDIA’s RTX 30 series and AMD’s RX 6000 series provide dedicated hotspot readings.
These sensors allow the system to:
- Identify the maximum temperature at any point on the die.
- Adjust cooling dynamically, such as increasing fan speeds.
- Throttle performance if necessary to prevent thermal damage.
The GPU hotspot value often runs 10°C to 20°C higher than the reported core temperature, making it a vital metric for anyone serious about system health.
Why Is Monitoring the GPU Hotspot Important?
Neglecting to monitor GPU hotspot temperatures can lead to significant problems:
- Thermal Throttling: When temperatures exceed safe thresholds, the GPU automatically reduces its clock speeds to cool down, resulting in performance loss.
- Hardware Degradation: Consistent exposure to high temperatures accelerates the wear of semiconductor materials, shortening the GPU’s lifespan.
- System Instability: Frequent crashes, visual artifacts, and system freezes can occur when thermal management is inadequate.
By keeping an eye on the hotspot, users can ensure that their GPU operates safely and efficiently, maintaining both performance and durability.
Ideal GPU Hotspot Temperature Range
Manufacturers typically design GPUs to handle hotspot temperatures up to 110°C safely, but optimal performance is achieved when the hotspot remains well below this limit. Here’s a general guide:
Keeping the hotspot temperature below 90°C during gaming is advisable to ensure long-term GPU health.
Common Symptoms of GPU Hotspot Issues
Identifying when a GPU hotspot becomes problematic can save users from irreversible damage. Typical symptoms include:
- Frequent Game Crashes: Especially in GPU-intensive titles.
- Frame Rate Drops: Unexplained dips in performance during gameplay.
- Loud Fan Noise: Fans spinning at full speed continuously.
- Screen Artifacts: Visual distortions or flickering.
- System Shutdowns: Thermal protection mechanisms kicking in to prevent damage.
Best Methods to Reduce GPU Hotspot Temperature
1. Improving Case Airflow
Proper case ventilation is essential. Upgrading intake and exhaust fans ensures that hot air does not accumulate inside the chassis, helping to lower the GPU temperature overall.
Tips:
- Use high-quality, high-CFM fans.
- Maintain positive air pressure to minimize dust buildup.
- Arrange cables neatly to avoid airflow obstruction.
2. Reapplying Thermal Paste
Replacing the stock thermal paste with a high-performance compound can significantly enhance heat transfer between the GPU die and the cooler.
Procedure:
- Carefully dismantle the GPU (voiding warranty risks).
- Clean off old paste using isopropyl alcohol.
- Reassemble the cooler securely.
3. Undervolting the GPU
Undervolting involves reducing the voltage supplied to the GPU without sacrificing much performance. Lower voltage means less heat generation, leading to a cooler hotspot.
Software Tools:
- MSI Afterburner
- AMD Radeon Software
- NVIDIA Inspector
4. Upgrading GPU Cooling Solutions
Installing a better cooling system such as a hybrid cooler (air + liquid) or a full custom water block can bring substantial temperature improvements.
Benefits:
- Quieter operation.
- Lower overall and hotspot temperatures.
- Potential for higher stable overclocks.
5. Regular Maintenance
Dust accumulation can block heat sinks and slow fans, leading to hotspot formation. Regularly cleaning the GPU and fans ensures consistent thermal performance.
Maintenance Tips:
- Use compressed air to clean vents and fans monthly.
- Replace dust filters or clean them regularly.
- Monitor fan health and replace failing fans promptly.
Should You Be Worried About a High GPU Hotspot Temperature?
If the hotspot consistently exceeds 100°C during normal usage, it is a cause for concern.
While modern GPUs have robust thermal protections, operating at such temperatures accelerates thermal degradation.
Immediate measures should be taken to bring temperatures down, including improving cooling and potentially underclocking the GPU if necessary.
How Manufacturers Address GPU Hotspot Problems
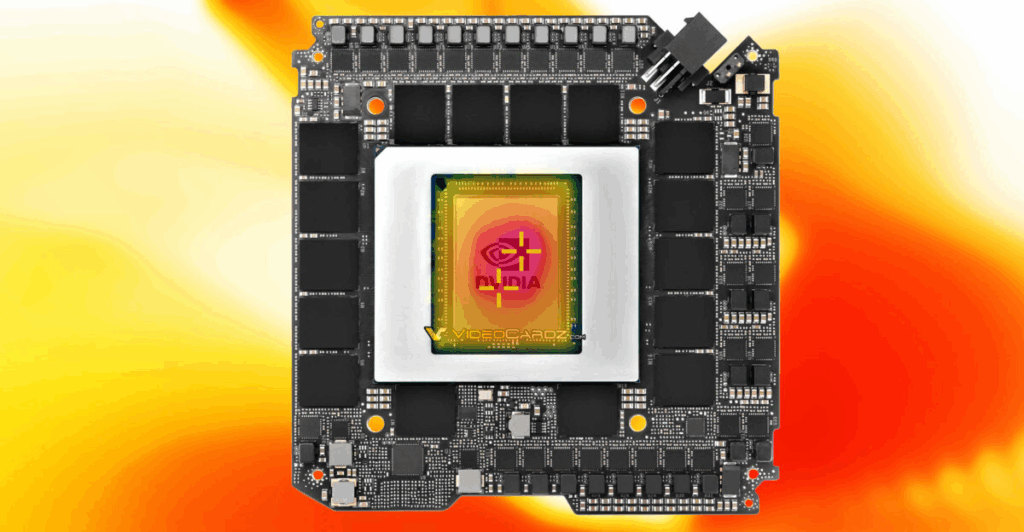
GPU manufacturers like NVIDIA and AMD implement several technologies to manage hotspot issues:
- Dynamic Fan Profiles: Adjust fan speeds based on real-time hotspot readings.
- Advanced Thermal Sensors: Spread across the die for accurate detection.
- Vapor Chamber Cooling: Evenly distributes heat across the cooler.
- Thermal Throttling Algorithms: Protect the GPU from permanent damage.
Future advancements are focused on even more intelligent thermal management systems to optimize performance under varying loads.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Is a GPU hotspot of 110°C safe?
Most modern GPUs, like AMD’s RX series, are designed to tolerate hotspot temperatures up to 110°C.
However, consistently reaching 110°C can shorten GPU lifespan and may indicate cooling inefficiency that should be addressed.
How do I check my GPU hotspot temperature?
You can monitor your GPU hotspot temperature using tools like HWInfo, GPU-Z, or software from your GPU manufacturer, such as NVIDIA GeForce Experience or AMD Radeon Software.
Can high GPU hotspot temperature cause performance loss?
Yes, a high GPU hotspot temperature can trigger thermal throttling, where the GPU reduces clock speeds to cool down, resulting in lower gaming performance or rendering speeds.
What causes an abnormal GPU hotspot temperature?
Factors like poor case airflow, dust buildup, worn-out thermal paste, overclocking, or a failing cooling system can lead to abnormally high GPU hotspot temperatures.
How can I lower my GPU hotspot temperature?
To lower GPU hotspot temperatures, improve case airflow, clean your GPU and fans, reapply thermal paste, or upgrade to a more efficient cooling solution like a liquid cooler or a better air cooler.
Is GPU hotspot temperature important to monitor?
Yes, monitoring the GPU hotspot temperature is crucial to ensure your GPU operates within safe limits, avoiding overheating, system crashes, and long-term hardware damage.
Conclusion:
At the end of the conclusion,
Monitoring and managing GPU hotspot temperatures is essential for maintaining optimal performance and extending the hardware’s lifespan. Consistent cooling practices and regular maintenance help prevent overheating and system instability.



Post Comment